Chemistry of Natural
Products
Name : Lina Purwanti
Student number :
RSA1C110009
Study Program : Chemistry Education of ISSTE
1. Jelaskan
dalam jalur biosintesis triterpenoid, identifikasilah faktor-faktor penting
yang sangat menentukan dihasilkannya triterpenoid dalam kuantitas yang banyak.
Answer :
Triterpenoid carbon skeleton is a
compound derived from six isoprene units and the biosynthesis derived from C30
acyclic hydrocarbons, ie skualena.
SYNTHESIS TERPENOID
Terpenoids is a form of the compound
with large structures in natural product-derived and isoprene unit (C5) are
coupled in the model head to tail, whereas isoprene units derived from acetic
acid metabolism by mevalonic acid pathway (MVA). The reaaksinya are as follows:
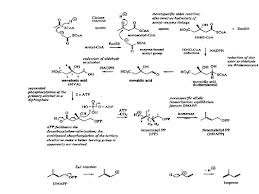
Figure 1 Line Acetate is the formation of IPP formation of terpenoids Via
Bricks mevalonic acid (http://nadjeeb.wordpress.com).
In general, the biosynthesis of
terpenoids with the three basic reactions, namely:
1. Formation of active isoprene
derived from acetic acid via mevalonic acid.
2. Merging head and tail of two
isoprene units to form mono-, seskui-, di-. Sester-, and poly-terpenoids.
3. The incorporation of the tail and
the tail unit C-15 or C-20 produces triterpenoids and steroids.
The mechanism of the reaction steps
of terpenoid biosynthesis is activated by acetic acid as coenzyme A did produce
acid Claisen type condensation asetoasetat.
Compounds produced by the
condensation of acetyl coenzyme A did produce aldol type branched carbon chains
as found in mevalinat acid, subsequent reactions are fosforialsi, elimination
of phosphoric acid and dekarboksilasi produce isopentenyl (IPP) who later
became dimethyl allyl berisomerisasi piropospat (DMAPP) by the enzyme
isomeriasi. IPP as active isoprene unti joined head to tail with DMAPP and this
merger is the first step of the polymerization of isoprene to produce
terpenoids.
This merger occurs because electrons
attack the double bond carbon atoms of IPP to DMAPP electron deficient followed
by the removal of ions that produce geranil. pirofosfat pyrophosphate (GPP) is
an intermediate for all monoterpenoid compounds. Merger between one unti
further IPP and GPP with the same result menaisme Farnesil pyrophosphate (FPP),
which is an intermediate for all compounds seskuiterpenoid. Diterpenoid compounds
derived from geranil-geranil Pyrophosphate (GGPP) derived from the condensation
between one unti IPP and GPP by the same mechanism. The mechanism of
biosynthesis of terpenoid compounds are as follows:
From that picture
in biosynthesis we can get if there is enzyme such as isomeriasi enzyme to help
reaction faster, Co-A to make active acetic acid so will happen condensation, H2O,
and acetic acid
2. Jelaskan
dalam penentuan struktur flavonoid, kekhasan signal dan intensitas serapan
dengan menggunakan spektrum IR dan NMR. Berikan dengan contoh
sekurang-kurangnya dua struktur yang berbeda.
Answer :
IR Spectroscopy : This section takes you through typical IR spectra of compounds with
different functional groups to help you recognize distinctive, characteristic
IR bands. The final section outlines how to analyze any IR spectrum.
Infrared spectrophotometer can be used for the following:
a. Identfcation functional group
b. Taking into account the presence of
other information such as melting point, boiling point, molecular weight and
refractive index to determine the structures and to identify compounds
c. By using a computer, can identify
compounds even mixture of compounds.
infrared spectrophotometry is more widely used for
identification of a compound through the group functions. For the purpose of
structure elucidation, the wavenumber region 1400 - 4000 cm-1 which is at the
left-ir spectrum, an area that is particularly useful for the identification of
functional groups, which is the absorption of the stretching vibration.
Furthermore, the area just to the right of wave numbers 1400 cm-1 are often
very complicated because in this region occurred absorption of stretching
vibration and bending vibration, but any organic compound having a
Characteristic absorption in this region. It is therefore part of the spectrum
is called fingerprint region (fingerprint region). Currently there are two
kinds of instruments that ir spectroscopy and FTIR (furier transformation infra
red). FTIR is more sensitive and accurate example to distinguish cis and trans
forms, conjugated and isolated double bonds and others are in the ir
spectrophotometer indistinguishable.
The Theory of NMR: This section explains the theory of NMR spectroscopy at a level
appropriate for the sophomore organic chemistry student. Both proton and carbon
NMR are covered.
As the name implies NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance, nuclear
magnetic resonance), NMR spectroscopy related to the core character of an
atom in a molecule is analyzed. NMR spectrometry is basically another form of
absorption spectroscopy as well as UV-VIS and IR. The difference with IR and
UV-VIS is
Absorption system under the influence
of a magnetic field and it is not on UV-VIS and IR. In the NMR energy
electromagnetic radiation in the radio frequency region.
Working Principle of NMR Spectroscopy
This type of spectroscopy method is
based on the absorption of energy by spinning particles in a strong magnetic
field. The energy used in the measurement by this method is in the region from
75 to 0.5 m or radio waves at a frequency of 4-600 MHz, depending on the type
of core that is measured.
Core that can be measured by NMR,
namely:
a. spherical shape
b. spin
c. Spin quantum number = ½
d. Odd number of protons and
neutrons, for example: 1H, 19F, 31P, 11B, 13C
In the magnetic field, NMR active
nuclei (eg 1H or 13C) absorb at a frequency characteristic of an isotope. The
resonant frequency, energy absorption and the signal intensity is proportional
to the strength of the magnetic field. For example, at 21 tesla magnetic field,
protons resonate at 900 MHz. value of 21 T magnet is considered equivalent to a
900 MHz magnet, although different nuclei resonate at different frequencies.
At the Earth's magnetic field, the
same core resonate at audio frequencies. This phenomenon is exploited by the
Earth's field NMR spectrometers, which are cheaper and easier to carry. This
instrument is used for field work and teaching purposes.
IR/NMR Spectroscopy Problem : This section takes you through the steps that you will need
to do to solve for the structure of an organic compound given the IR, NMR, and
molecular formula. Each common functional group is discussed in turn and many
examples are presented.
3. Dalam isolasi alkaloid, pada tahap awal dibutuhkan kondisi
asam atau basa. Jelaskan dasar penggunaan reagen tersebut, dan berikan
contohnya sekurang-kurangnya tiga macam alkaloid.
answer :
An alkaline compound, derived from
plants and animals, generally have cicncin heterocyclic (not all members have
cincicn nitrogen) and often have biological activity in humans. Not all
diklasifikasan nitrogenous compounds as pyridine alkaloids example. Alkaloids
kbasaannya different in nature, some properties amfore cntohnya cephalin and
psychotrin or even acid recini example. Most dtemukan in plants, although it
has now been recorded as also found in fungi (ergot alkaloids), in animal musk
deer (muscopyridin), in bacteria p.aeruginosa and some synthetic products.
1. Presipitas Alkaloids
Most alkaloids are precipitated from
neutral or acidic solution by a number of reagents containing heavy metals such
as mercury (Hg), platinum (Pt), bismuth (Bi) and gold (Au), to form a bond with
their salt
Examples of precipitating reagent
alkaloid
a. Mayer's reagent (potassium mercury iodide)
Providing the most precipitation
creamy besa alkaloid
Caffeine and efredin only at high
concentrations.
Ricinin not give precipitation
b. Wagner's reagent (I / KI)
Providing brick red precipitate
against almost all alkaloids
c. Hager's reagent (picric acid solution is concentrated)
Give a
yellow precipitate
d. Dragendroff's reagent (solution of potassium bismuth iodide)
Giving up brownish reddish orange
color. Also used as a spray reagent for TLC identification alakaoit
e. Another Reagenisia using acid
Tannat, fosfomolibdat acid,
fosfotungstat
2. Specific color reagents
a. Erlich's reagent (Van-Urk reagent)
Solution of
p-dimethylaminobenzaldehide in acid, giving distinctive colors birun gray or
greenish with Ergot
b. Cerric ammonium sulphate (CAS) under acidic
Alakaoid typical reagents for indole,
giving a yellow or reddish orange.
c. Vitali-Mari reagent: characteristic for alkaloids tropan
d. Thaleoquine reaction: typical for alkaloid sinkona
e. Murexide reaction: typical for purine bases
in the first step alkoloid isolation
we need acid and base condition. In acid because adding organic acid will make
extract produces salt and adding base to lose salt bonding to be free alkaloida
Answer :
between the three aspects are closely linked, the boisintesis
used to obtain new compounds or techniques such as structural changes in the
biosynthesis of catechins using 3 x malonyl-CoA will result coas. the
biosynthesis of these alone we can use in determining the structure of such ir,
uv, and nmr. and for the isolation itself is to recall the components or the
active ingredient by using certain solvents. of the insulation itself, we can
also determine its structure. if the structure between isolation and
biosynthesis have been obtained, the results can be compared
example :
EXTRACTION
Extraction is a way to separate a
mixture of several substances into separate components (Winarno et al. 1973).
According to Hunt (1988), extraction is a method of separation of one or more
of the desired compound or solid solution containing a mixture of such
compounds both physically and chemically.
In the process of extraction, solvent
diffusion event occurs in the cell material. Solvent into the cell material
will dissolve the compound when the solubility of the compound, which is
extracted with solvents. In this way will be achieved equilibrium between the
solute and solvent. Spending the active ingredient of the material depends on
the rate of diffusion of the substance of substances into the solvent, the
contact time, and the rate of solvent through the material (Bombardelli 1991).
Harborne (1987) states that the
solubility of a substance in a solvent depends on the polarity. The only polar
substances soluble in polar solvents as well as non-polar substances only
soluble in nonpolar solvents. Selection of solvent in the extraction solvent
should pay attention selectivity, the ability to extract the target component,
toxicity, ease evaporated, and the price of solvent.
Isolation of Alkaloids
Alkaloid extracted from the leaves of plants, flowers, fruit,
bark, and roots are dried and then crushed. Extraction of alkaloids in general
are as follows:
a. Alkaloid extracted with solvents, eg ethanol, and then
evaporated.
b. Extracts were obtained inorganic acids to produce a
quaternary ammonium salt and then extracted again.
c. Quaternary ammonium salt obtained was treated with sodium
carbonate to produce these alkaloids were then extracted with a solvent-free
such as ether and chloroform.
d. Mixture - a mixture of alkaloids obtained finally
separated in various ways, such as chromatographic methods (Tobing, 1989).
There are other ways to get the
alkaloids from the acid solution by absorption using Lloyd reagent, and then
eluted with dilute alkali alkaloids. Alkaloid that is hydrophobic absorbed by
XAD-2 resin and then eluted with acid or ethanol-water mixture. Many alkaloids
which can be precipitated by Mayer's reagent (potassium mercury (II) iodide) or
salt Reineccke.
This study used a general way that
the isolation of alkaloids extracted with an organic solvent, acidification,
formation of quaternary ammonium salts with bases, extraction with organic
solvents, and purification using column chromatography, thin layer
chromatography, or electronic instruments (IR, GC-MS , UV-Vis)
So after we get isolation results
obtained then the structure can be determined